Autonomous Driving Perception System
Deep learning-based 2D semantic segmentation and 3D object detection for intelligent vehicles
Overview
A comprehensive autonomous driving perception system integrating advanced 2D semantic segmentation and 3D object detection algorithms. This project was completed during my internship at Chongqing Zhongke Automotive Software Innovation Center, focusing on the core perception technologies for intelligent vehicles. The system demonstrates the complete pipeline from dataset construction through IsaacSim simulation to real-vehicle deployment, showcasing practical implementation of state-of-the-art deep learning algorithms in autonomous driving scenarios.
Technical Achievements: Real-time semantic segmentation with pixel-level accuracy, robust 3D object detection under various weather conditions, and successful deployment from simulation to real-vehicle testing with comprehensive validation framework using MMSegmentation and MMDetection3D frameworks.
System Demonstration
Technical Architecture
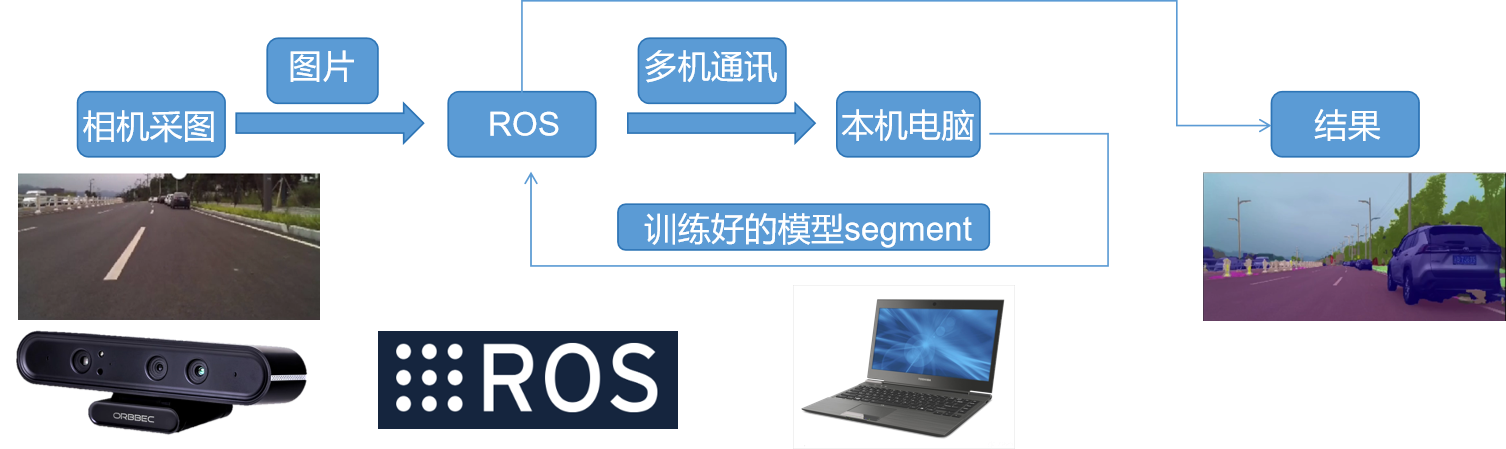
Technology Stack Overview
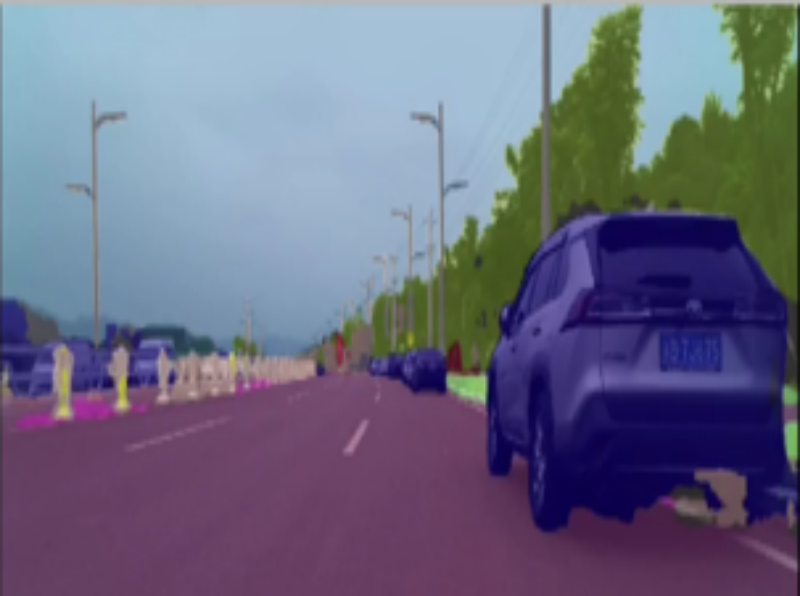

2D Semantic Segmentation
🎯 Pixel-level understanding
🚗 Road scene parsing
⚡ Real-time processing
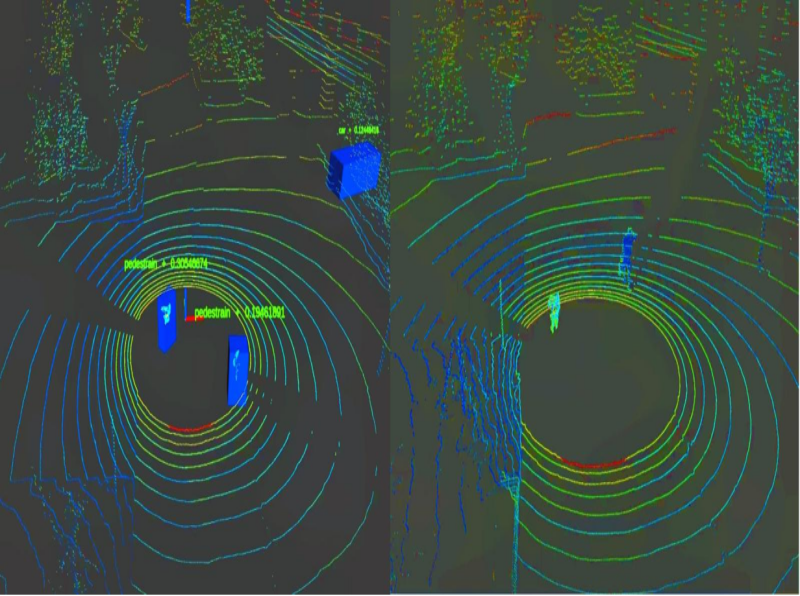
3D Object Detection
📏 Spatial localization
🎯 Multi-class detection
📊 Distance estimation
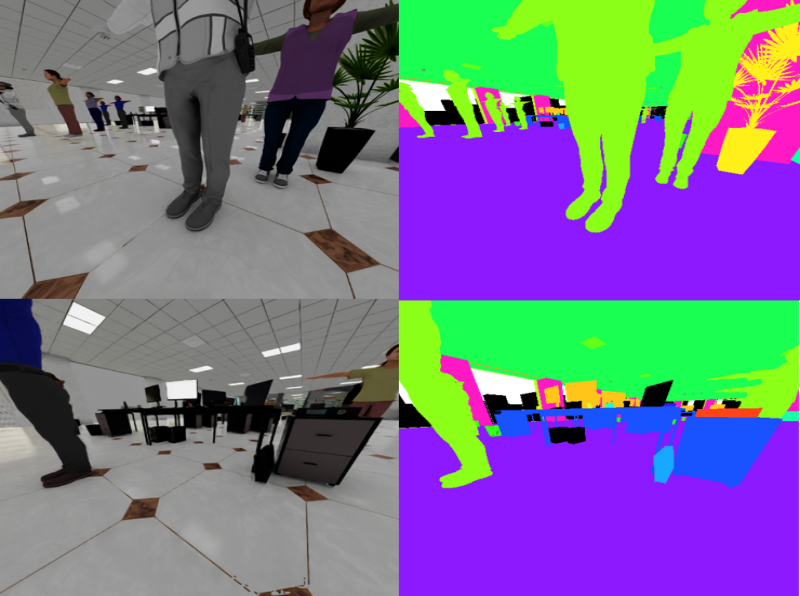
IsaacSim Validation
🌐 Virtual testing
🔄 Parameter tuning
✅ Safe validation
Core Technologies
1. Advanced 2D Semantic Segmentation
Framework Integration: Built upon MMSegmentation, leveraging state-of-the-art segmentation algorithms including PSPNet, DeepLabV3+, and Swin Transformer-based architectures optimized for automotive scenarios.
The semantic segmentation module performs pixel-level scene understanding across 19 distinct semantic classes, including road boundaries, vehicles, pedestrians, traffic signs, and drivable areas. The implementation leverages advanced deep learning architectures that have been specifically optimized for automotive applications, ensuring both accuracy and computational efficiency. Model quantization and TensorRT optimization techniques enable real-time deployment on NVIDIA Xavier platforms while maintaining high segmentation quality.
Domain adaptation plays a crucial role in ensuring robust performance across diverse driving environments. The system employs fine-tuning strategies that adapt pre-trained models to specific driving scenarios, enhancing generalization capabilities across urban, highway, and rural settings. This approach significantly improves the system’s ability to handle varying lighting conditions, weather patterns, and road surface types encountered in real-world autonomous driving scenarios.
2. 3D Object Detection Integration
Framework Integration: Implemented using MMDetection3D with point cloud processing techniques, the 3D object detection component complements the 2D semantic segmentation system by providing spatial awareness capabilities.
The 3D detection system processes LiDAR point cloud data to achieve spatial localization of surrounding objects. The implementation incorporates multi-modal fusion techniques that combine camera RGB data with LiDAR point clouds, enhancing overall perception accuracy. This component serves as a supplementary module to the primary 2D semantic segmentation system, providing additional depth information for comprehensive scene understanding.
3. Simulation-to-Reality Pipeline
The project establishes a comprehensive validation framework that bridges the gap between simulation and real-world deployment through advanced domain adaptation techniques. NVIDIA IsaacSim provides a photorealistic simulation environment with accurate physics modeling, enabling extensive algorithm testing in safe virtual environments before real-vehicle deployment.
The simulation platform supports large-scale scenario generation, allowing for systematic evaluation of edge cases and rare driving situations that are difficult to encounter during traditional road testing. Advanced data augmentation and style transfer techniques help minimize the domain gap between simulated and real-world data, ensuring that algorithms trained or validated in simulation perform reliably when deployed on actual vehicles.
Performance Metrics & Validation
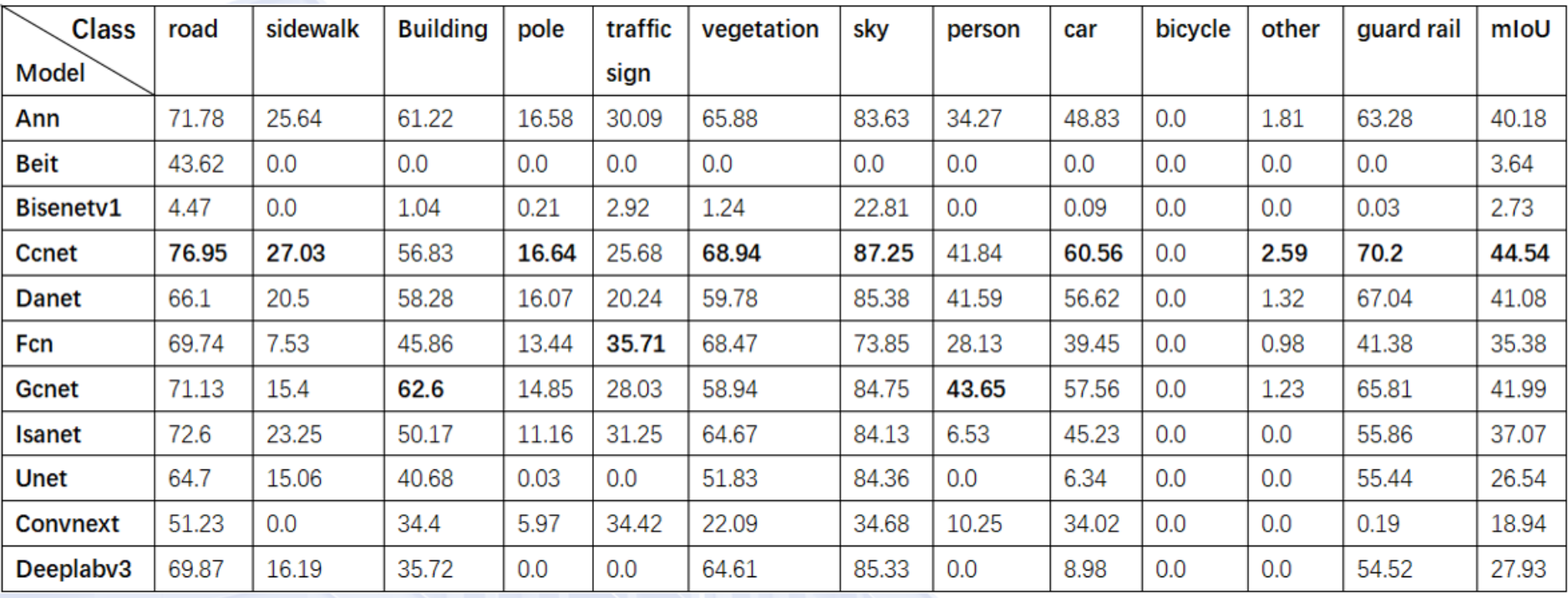
Evaluation Framework
The performance evaluation system encompasses multiple dimensions to ensure comprehensive assessment of the autonomous driving perception capabilities. Detection accuracy assessment focuses on the system’s ability to correctly identify and classify various objects in complex traffic scenarios, with particular emphasis on critical safety-related targets such as vehicles, pedestrians, and traffic infrastructure.
Real-time processing requirements form a crucial aspect of the validation framework, as autonomous driving systems must operate within strict latency constraints to ensure safe operation. The system demonstrates consistent performance under varying computational loads while maintaining the necessary processing speeds for real-time decision making in dynamic traffic environments.
Robustness testing across diverse environmental conditions validates the system’s reliability under challenging scenarios including adverse weather conditions, varying lighting situations, and complex traffic patterns. The evaluation protocol systematically assesses performance degradation patterns and identifies operational boundaries to ensure safe deployment in real-world applications.
Dataset Construction & Training
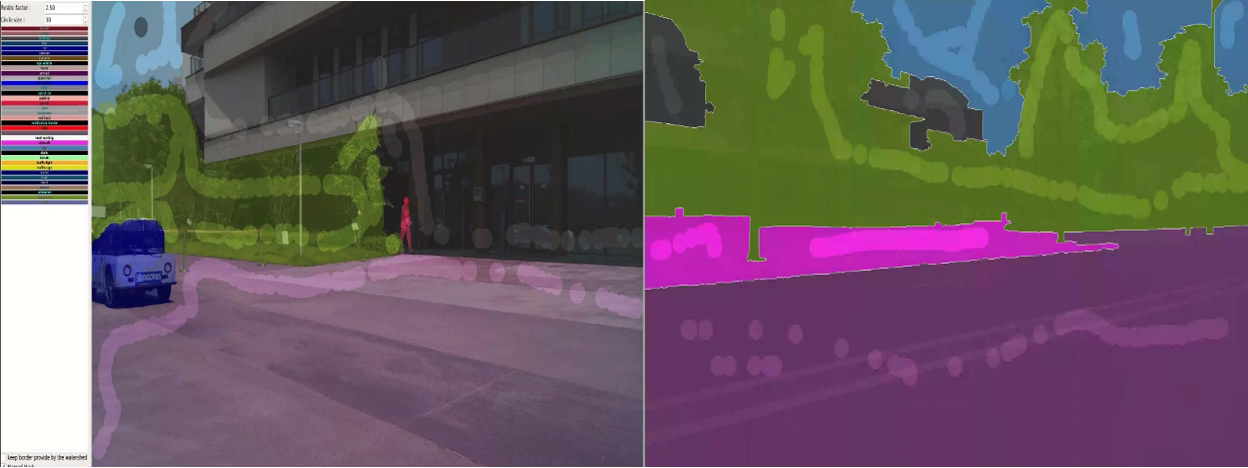

Data Collection Strategy
The dataset construction process followed a systematic approach to ensure comprehensive coverage of real-world driving scenarios. Data collection encompassed urban intersections with complex traffic patterns, high-speed highway environments with lane changes and merging scenarios, and rural roads presenting unique challenges such as unmarked boundaries and varying surface conditions. This multi-scenario approach ensures that the trained models possess robust generalization capabilities across diverse driving environments.
Weather condition diversity represents a critical aspect of the dataset design, incorporating sunny conditions with clear visibility, rainy scenarios with reduced visual clarity, foggy environments with limited range perception, and night-time driving situations with challenging lighting conditions. Each weather condition presents unique challenges for semantic segmentation algorithms, requiring specialized adaptations and robust feature extraction techniques.
The annotation process utilized professional-grade tools to ensure high-precision pixel-level semantic annotations. Quality control measures included cross-validation by multiple annotators and systematic review processes to maintain annotation consistency. Advanced data augmentation techniques were employed to artificially expand the dataset size while preserving semantic correctness, including geometric transformations, color space variations, and synthetic weather condition simulation.
Real-World Deployment & Testing
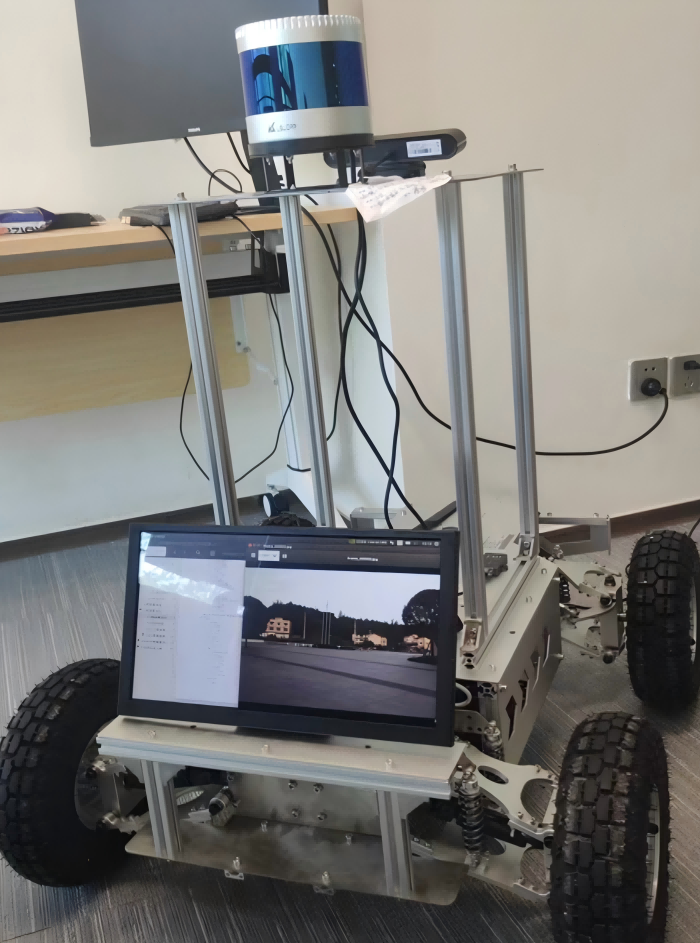

Testing Validation Framework
The urban environment testing phase focused on the most challenging aspects of city driving, including navigation through complex intersections with traffic signal recognition capabilities. The system demonstrated robust performance in dense pedestrian and vehicle traffic scenarios, successfully identifying and segmenting multiple objects simultaneously. Construction zones presented particular challenges due to temporary traffic patterns and unusual obstacle configurations, yet the system maintained reliable detection and segmentation performance.
Highway scenario validation emphasized high-speed performance at velocities exceeding 60 km/h, where rapid decision-making and extended detection ranges become critical. The system successfully handled lane changing and merging maneuvers, demonstrating its ability to segment road boundaries and identify vehicles across different lanes while maintaining accurate predictions. Long-range object detection capabilities proved essential for highway safety, with the system consistently segmenting and classifying objects at distances exceeding 60 meters.
Adverse weather condition testing revealed the robustness of the semantic segmentation approach. Rain and fog conditions, which typically degrade camera performance, were effectively handled through specialized preprocessing and model adaptation techniques. Night-time testing demonstrated the system’s ability to operate effectively under challenging lighting conditions, leveraging optimized low-light image processing techniques and robust feature extraction methods.
Technical Innovation & Contribution
Key Achievements
Algorithm Innovation: The project successfully adapted state-of-the-art academic models for real-world automotive deployment, addressing the significant challenges associated with transitioning from controlled research environments to safety-critical applications. The development of efficient semantic segmentation techniques represents a substantial contribution to autonomous driving perception technology. These methods leverage advanced deep learning architectures while maintaining computational efficiency for real-time deployment.
The implementation of robust domain adaptation methods for simulation-to-reality transfer addresses one of the most challenging aspects of autonomous driving system development. The techniques developed enable effective utilization of simulation environments for algorithm training and validation while ensuring reliable performance when deployed on real vehicles. This approach significantly reduces development time and costs while maintaining high safety standards.
Engineering Excellence: Achieving real-time performance on embedded automotive computing platforms required extensive optimization work, including model compression, quantization, and hardware-specific acceleration techniques. The comprehensive validation pipeline established during this project spans from initial simulation through real-vehicle testing, providing a robust framework for future autonomous driving system development.
The demonstration of industry-competitive accuracy metrics across diverse driving scenarios validates the practical applicability of the developed technologies. Performance consistency across urban, highway, and rural environments, combined with robust operation under various weather conditions, demonstrates the maturity of the implemented perception system.
Research Impact: This project contributed significantly to understanding the practical challenges associated with autonomous driving perception system deployment. The experience gained in bridging the gap between academic research and industrial application provides valuable insights for future research directions. The development of expertise in safety-critical AI system validation and deployment represents a substantial contribution to the field of autonomous driving technology.
Technical Stack & Infrastructure
The hardware platform integrates multiple high-resolution cameras providing comprehensive visual scene understanding from multiple perspectives. The 64-beam Velodyne LiDAR system delivers high-resolution 3D point cloud data with exceptional range and angular resolution, supporting the overall perception framework. The NVIDIA Xavier AGX computing platform provides the computational power necessary for real-time deep learning inference while meeting automotive power consumption and thermal constraints.
High-precision GPS and IMU navigation systems provide essential localization and motion information, enabling accurate sensor data fusion and coordinate frame transformations. The real-time data acquisition and storage system ensures synchronized capture of all sensor modalities while providing sufficient bandwidth for high-frequency data logging during extensive testing scenarios.
The software framework builds upon industry-standard tools and libraries, with MMSegmentation providing a robust foundation for semantic segmentation tasks. NVIDIA IsaacSim serves as the primary simulation platform, offering photorealistic rendering and accurate physics simulation for comprehensive algorithm validation. PyTorch provides the deep learning framework foundation, while ROS enables seamless system integration and inter-process communication across the autonomous driving software stack.
This project demonstrates the successful application of deep learning, computer vision, and autonomous systems to solve complex real-world perception challenges in intelligent vehicles. The comprehensive approach from research to deployment showcases the complete development cycle of safety-critical AI systems in the automotive industry, providing valuable insights into the practical challenges and solutions for autonomous driving technology.